Condensate Polishing
Impurity Removal Of Process and Feed Water

The DS21 Condensate Polishing Package reduces the risk of damage to main systems caused by the concentration of soluble impurities.
DS21’s Condensate Polishing packages are designed to remove contaminates that corrode internals and contribute to insoluble impurities such as copper, iron and silica in the re-circulating stream.
Exploring Solutions for Condensate Polishing?
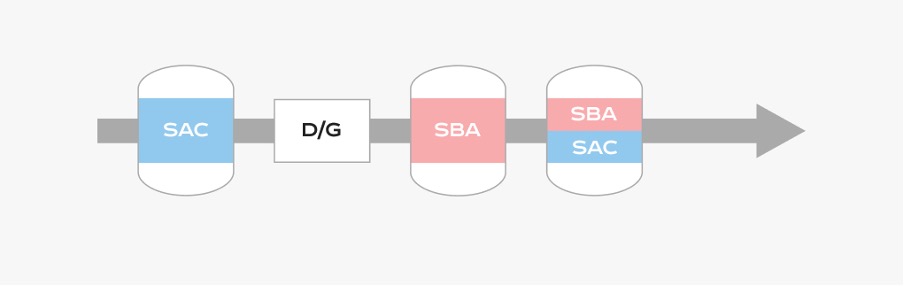
Condensate Polishing Process Flow

TECHNOLOGY
Technologies Overview
2B3T Ion Exchange System
Producing pure water through the combined use of a cation-exchange resin tower (C/E), decarbonation tower (Deg.) and anion-exchange resin tower.
Cation Exchanger
With cation-exchange resin packed in, removing cation constituents from the raw water.
Decarbonation Tower
Removing carbonic acid constituents from the water passing through C/E to reduce anion loading in A/E.
Anion Exchanger
With anion-exchanger packed in, removing anion constituents.

Pre-Filter (Activated Carbon Filter)
Activated carbon filters are generally employed in the process of removing organic compounds and/or extracting free chlorine from water, thereby making the water suitable for discharge or use in manufacturing processes. Eliminating organics in potable water, such as humic and fulvic acid, prevents chlorine in the water from chemically reacting with the acids and forming trihalomethanes, a class of known carcinogens.

Mixed Bed Polisher
A mixed bed ion exchanger (mixed bed polisher, mixed bed deionizer) is a vessel filled with a mixture of cation exchange resin and anion exchange resin for removal of trace dissolved solids from water. During service, water flows through this resin mixture. Cations dissolved in the water are then exchanged for hydrogen ions (H+), while anions dissolved in the water are exchanged for hydroxide ions (OH-). Hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions react to water.

